AERODESIGN
The Project Context
In a team of 10, we set out to compete in an aircraft design competition held at Florida, USA.
In a span of 14 months, we worked on 5 design iterations and fabricating over 10 working aircraft for contingencies for this competition. The rulebook presented a nexus of problems and design constraints. As a technical member of the team, I designed the tail and the wing, handled all the technical presentations, and worked on fabricating all the parts of the plane.
The team was awarded the 10th position overall out of 70 participants with 6th position on the technical presentation.

CFD analysis for lift and drag characteristics
Design Constraints
The design constraints on the aircraft were primarily for balancing the trade-off variables.
-
Flight score equation with variables like assembly time, empty weight, and payload fraction.
-
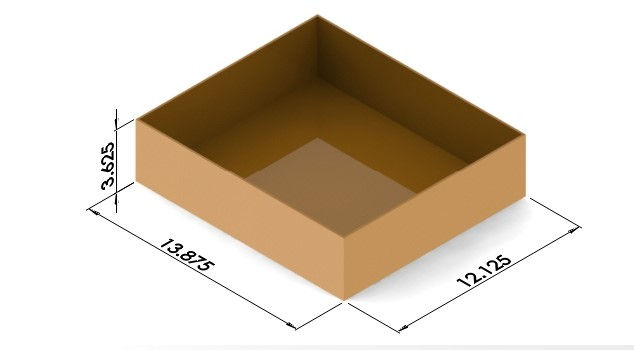
Maximum volume for the aircraft volume container.
-
Payload material restrictions.
-
Maximum battery capacity on the aircraft.
In conclusion, high payload being lifted and less empty weight as parameters would lead to a better score.
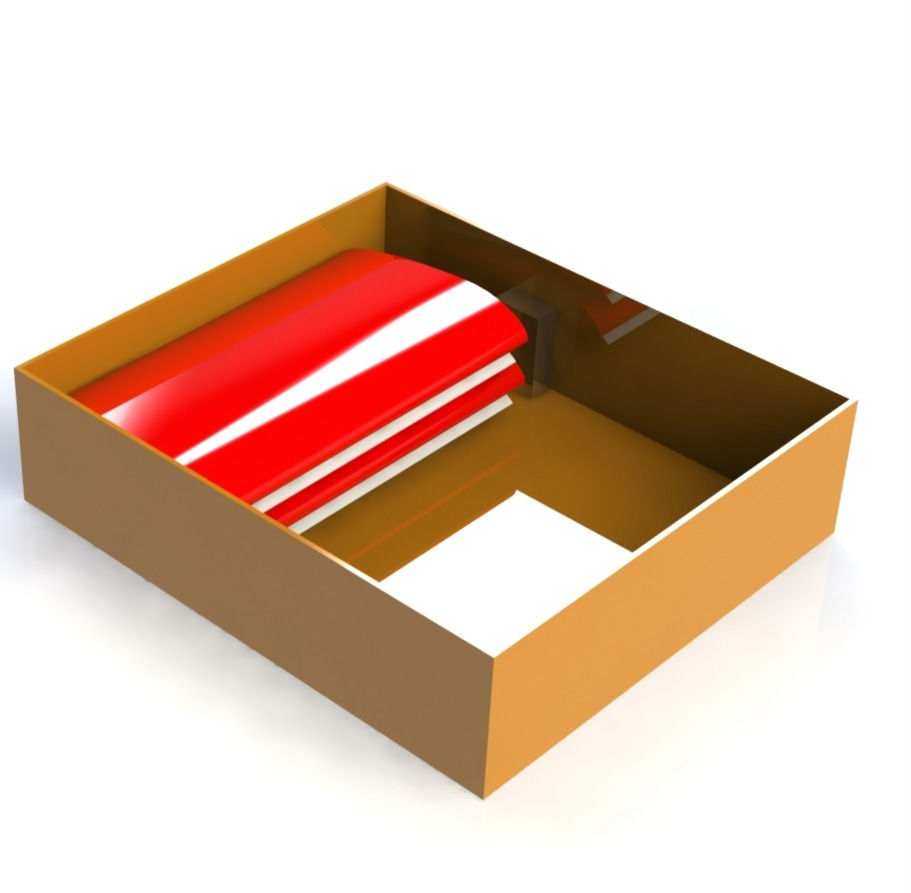
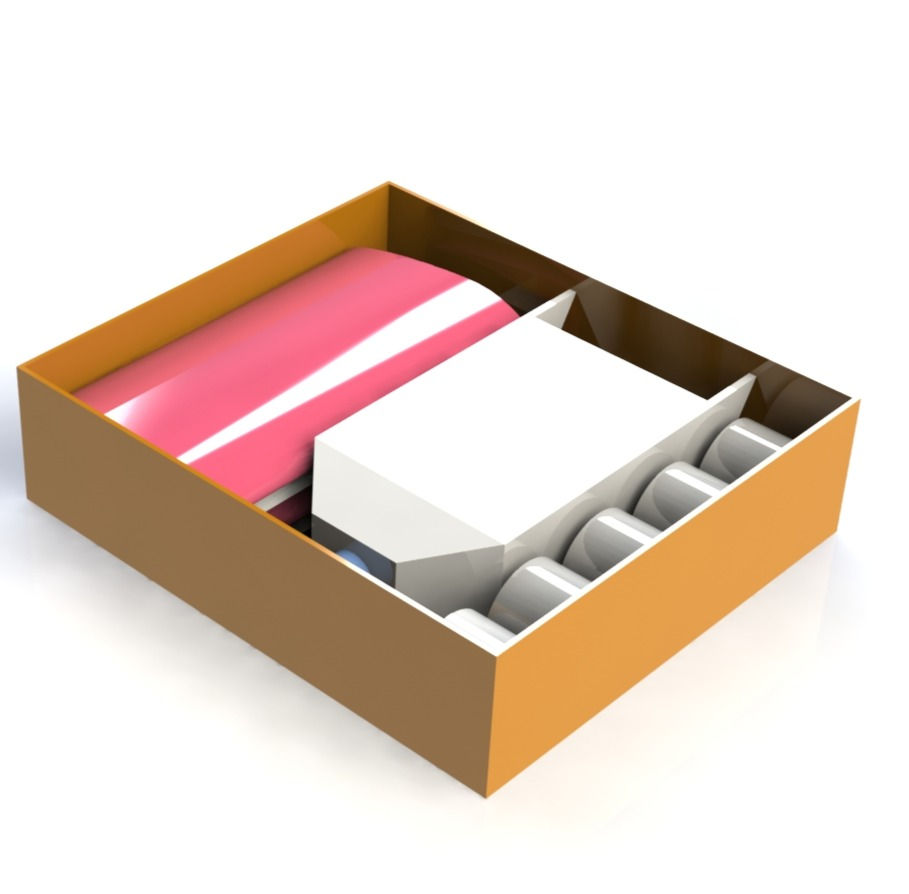



CAD for the aircraft disassembled in the constraint box
Testing and Analysis
For the problem of the difference between the rated and actual performance of the electronic components, I led the team in designing and fabricating a thrust test rig for the team. It helped in quantifying the battery capacity and the thrust for the selected equipment.
With every flight test, by using CFD structural analysis for the boom deformation and fluent analysis for the whole aircraft, the empty weight was consistently reduced.

Thrust test rig

Boom structural deformation

Pressure contour of the wing

Design Problems Solved
-
With the constraint box, a solid tail was out of the question while a detachable tail would lead to assembly time resulting in a low flight score. This problem was solved by making the tail deformable. The vertical tail was designed to bend onto the horizontal stabilizer hence occupying a minuscule space in the box and having a low assembly time.
-
Constraint box's largest dimension was 13.877 inches while the wingspan was 40.26 inches. This was solved by making the wings modular with 4 parts. To maintain the structural strength and uniformity, spars were used which ran along within the wings into each other.
-
The length of the aircraft was 25.236 inches. The problem was solved making the boom detachable with push rivets for quick integration.
-
Heat shields were removed from the electronics. They were rearranging close to the outer regions for natural cooling around the center of gravity to shed the extra weight and achieve a better score.
